
Balancing Risk

Patients are placed on anticoagulants to treat existing blood clots or reduce the risk of developing new blood clots. Unfortunately, anticoagulants increase the risk of bleeding. Balancing this risk of clotting and bleeding is essential for effective anticoagulation management.
The MAQI2 Process
Trained abstractors at participating sites enter clinical data into the MAQI2 registry, which is hosted and maintained by the Coordinating Center at the University of Michigan. MAQI2 compares bleeding and clotting event rates between participating sites, identifies and shares best practices, and works with sites to identify interventions to reduce adverse events and healthcare costs. Regular feedback is provided at quarterly meetings to help sites evaluate and adjust interventions. Achievement of pre-established goals is rewarded through Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan’s Value Partnerships program.
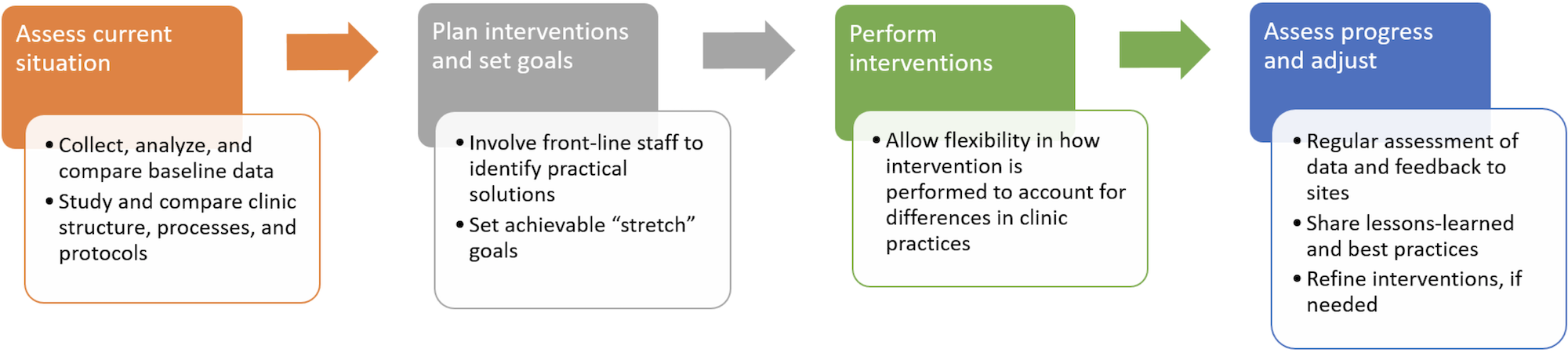
Aspirin Use
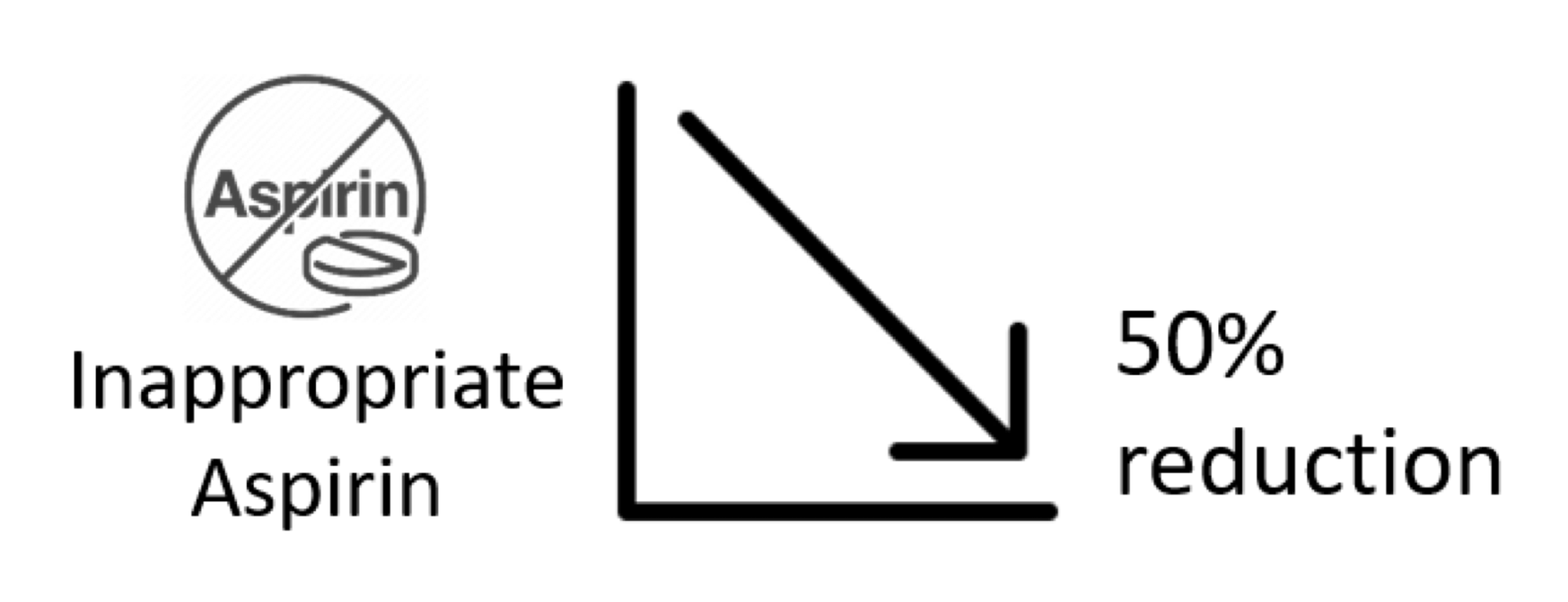
Reducing bleed risk in patients taking anticoagulants is very important. MAQI2 found that patients taking warfarin in combination with aspirin (another blood thinner) had twice the rate of bleeding with no clear clinical benefit. Over one-third of patients taking this combination did not have a clear reason to be taking aspirin. By developing systems to identify patients on inappropriate aspirin and coordination with providers, sites have been able to reduce inappropriate aspirin use by 50% in participating clinics since 2018, resulting in fewer bleeding events.
Unnecessary Labs
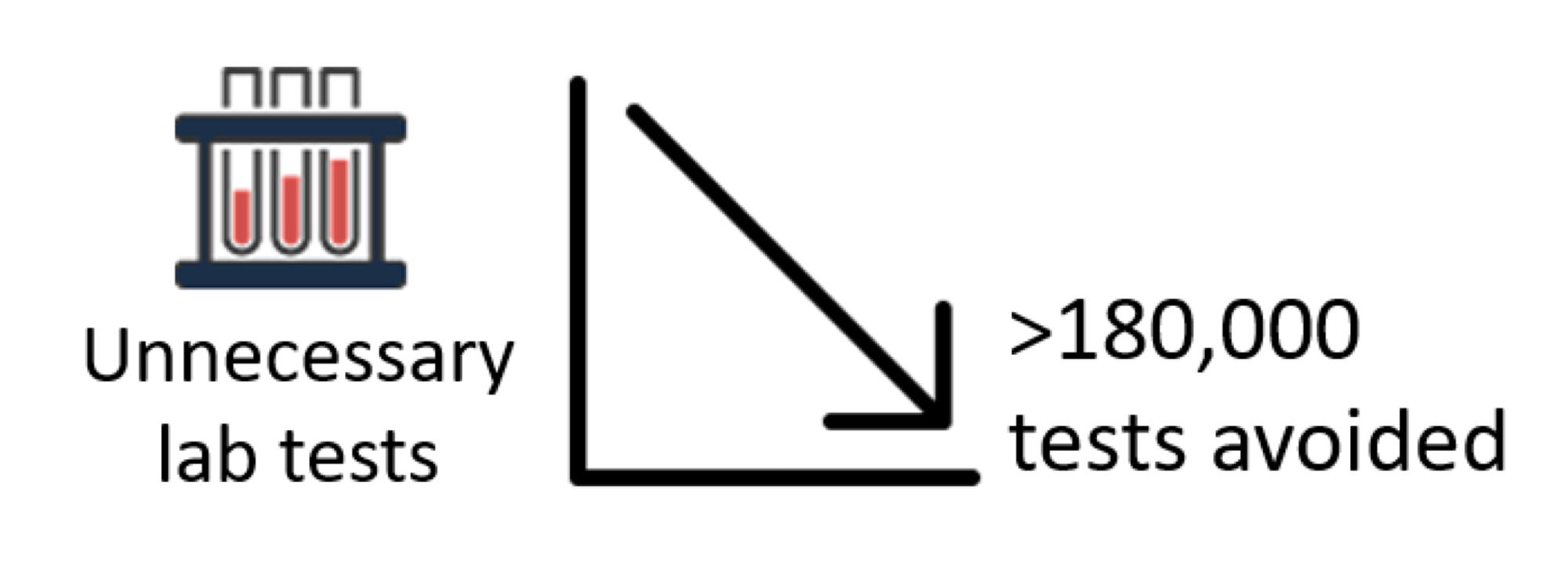
Patients taking anticoagulants require regular lab testing. Lab testing presents a burden to patients and health care providers and contributes to high health care costs. Recent guidelines suggest that certain patients can have less frequent lab testing without causing harm. MAQI2 sites modified management protocols to encourage less frequent lab testing. This has resulted in an estimated reduction of over 180,000 lab tests in participating clinics since 2017.
Patient Education Projects
Patient education is a very important component of safe and effective anticoagulation. Patients must be knowledgeable about how to take their anticoagulants, signs and symptoms of bleeding and clotting, and what to do in case they experience any of these adverse events. Since 2010, participating MAQI2 sites have made significant effort to improve the education provided to their patients.
Some examples of patient education initiatives:
- Development of an agreed-upon list of topics that patient education materials should include
- Patient education material review and revision based on the agreed upon required topics
- Monitoring the delivery of patient education materials to ensure that all patients receive educational handouts
- Translation of educational handouts into other languages
- Patient surveys to identify gaps in knowledge of anticoagulants
- Patient education videos